ESXi : Performing P2V Conversions using VMWare Converter
In order to convert a system it must be out of production – i.e. no transactions or processing can take place during the conversion.
I recently had to conduct around 60 P2V migrations to an ESXi cluster. The physical machines were on various subnets protected by firewalls that could not be modified ad-hoc to facilitate the migrations. I had two options:
1. Create rules for P2V communication; this requires (more information here: http://kb.vmware.com/selfservice/microsites/search.do?language=en_US&cmd=displayKC&externalId=1010056)
Source
|
Destination
|
TCP Ports
|
UDP Ports
|
|
|
Converter server
|
Source computer
|
445, 139, 9089, 9090
|
137, 138
|
|
|
|
Converter server
|
VirtualCenter
|
443
|
|
|
|
Converter client
|
Converter server
|
443
|
|
|
|
Source computer
|
ESX
|
443, 902
|
|
|
2. Use a conversion hub to bridge the required networks and act as the converter. This should be a Windows 2008 R2 VM with a VMXNET3 adapter connected to each network hosting physical machines )enabled on-demand, as required). The server should have RRAS installed as detailed below; this server must have an interface on the management network of the ESXi hosts.






Concepts;
3 servers are involved in the migration process;
- Source Server – the physical server you wish to convert to a virtual server
- ESX/Destination Server – the destination ESX host you wish to virtualise the physical server too.
- Converter Server – hostname vCONVERTER – Standalone Windows 2008 R2 with IP Routing Capabilities and VMware Converter – use RDP to access.
You have two options for the P2V conversion;
1. Online (with transactional processing stopped)
2. Cold Clone
For cold clone scenarios boot from the cold clone CD available and then proceed from step 6 under P2V Conversion. Things to bear in mind:
- You cannot ping the WindowsPE cold clone operating system, this is due to Windows Firewall. You can disable this using petool (supplied with cold clone ISO) – petool -i -f –disable
- The default gateway on the cold clone should be IP address of the vCONVERTER machine’s interface on the same subnet.
- You can inject SCSI/Network drivers into the coldclone iso file using petool, use ‘-n’ for network and ‘-d’ for storage; petool -i -n
Online P2V
Preparation
1. Reset the local administrator password on the source server, unless you are 100% sure you know the password.
2. Stop all transactional processing (SERVICES) on the source server and then configure service start-up as follows:
a. For SQL servers: set SQL services manual.
b. For Citrix use the cold clone CD
c. For a Domain Controller use the cold clone CD
3. On the source server capture all IP addressing and NLB information/configuration:
If the server is on a different subnet to the ESXi hosts you will need to configure host routes to facilitate firewall bypass:
For example:
- Physical host IP address: 172.20.20.152
- ESXi Server IP address: 10.144.120.1
- vCONVERTER ESXi Mgmt Network IP: 10.144.120.100
- vCONVERTER emote subnet IP address: 172.20.20.155
I. On the source server create a static host route to the ESXi server (change ESXi server IP address to suit), for example when EUVM01 (IP Address 10.144.120.1) is the destination – change the IP highlighted to suit:
route add 10.144.120.1 mask 255.255.255.255 172.20.20.155 -p
II. On the destination ESXi server create a static host route to the source server (change source server IP address to suit), for example when ECOMWA4 is the source server – change the IP highlighted to suit:
esxcfg-route -a 172.20.20.152/32 10.144.120.100

P2V Conversion
1. Logon to vcCONVERTER using Remote Desktop.
2. Enable the additional NIC that is valid for your required conversion, at the very least you require the following NICs to be enabled:
a. VMGMT-NETWORK-10.144.120.100-VLAN120
b. INTERNAL

3. Open the VMWare Converter Standalone Client from the desktop:

4. Select connect to local server and click ‘Login’

5. Click the Convert Machine button to proceed:

6. Enter the source server name or IP address, authentication details and then click ‘Next.’ You may be prompted to install the VM Conversion agent, proceed; however this may reboot the server.



Once installed manually reboot the server.
7. You will then be prompted to select a destination host. Because we have vApps the old converter crashes when you connect to the vCenter – If you do the converter will crash and you will have to start again!

8. Enter the desired VM name (just the hostname, not FQDN), select the correct storage pool and ensure that the VM version is ‘Version 7’

9. You are now able to modify the hardware that the virtual machine will be allocated; click EDIT next to any of the groups (Network etc) to begin the customisation.

Firstly configure the NIC VLAN membership; do not create teams etc.
- Un-tick the ‘Connect at power on’ option.
- Do not worry about selecting the correct VLAN/Network at this stage, for some reason this is ignored during the conversion process.

10. Now reduce the CPU count to 1 or 2(MAX) depending on function of the server.

11. Finally increase/decrease the storage allocation for each LUN, beware there are three type of clones that can occur:
1. Disk-based Block-Level (Disk-based)
Available during a cold clone only; disks are copied to the destination block by block.
2. Volume-based Block-Level (Volume-based)
Examine the source partition to determine what the partition boundaries are on-disk and then copy just the selected partitions on to the target disk on a block-by-block basis
3. Volume-based File-Level (File-level)
Converter creates the target disk, partitions and formats it appropriately and copies over data from the source to the target on a file-by-file basis
If you reduce the size of a volume it will use the Volume-based File-Level method; typically this is around 5-10 times slower. In a trial conversion of a BL35p we saw Volume-based Block-Level run at around 18MB/sec and Volume-based File-Level run at around 100-300KB/sec. Disabling anti-virus, defragging the volume may help to speed up Volume-based File-Level clones.
Select Advanced

12. If the server has 2 partitions split these into different vDisks as it will make future growth exercises far easier, click the Add Disk, then click the ‘Move Down’ – do this for each partition.

You can, if desired, perform a ‘Thin’ P2V using the option available here under the ‘Type’ column select the drop-down box to change disk format to thin.
13. Service Management:
a. If server is a Citrix Server set all Citrix services to ‘Manual’
b. If this is a SQL Server set all SQL services to Manual
c. Disable all HP (or similar OEM) Hardware/Management Services:

14. Finally select the ‘Power off source machine’ and ‘Install VMWare Tools…’ options, then click ‘Next.’

15. Review the task you are about to initiate, then click Finish – you may be prompted to reboot the source server, click Yes to reboot – the conversion will start automatically after the reboot.


16. Once the VM conversion has finished power on the VM and then allow the server to reboot automatically once it has installed the VM tools, you’ll be prompted to select a host to power on the VM on:

17. If the physical server was a Windows 2000 server, check that it is not stuck on the ‘It is now safe to turn off your computer’ screen. Physically power it off and remove from the rack/chassis.
18. If server was IDE based you will need to perform the steps here and modify the vmdk files so that the adapterType is not IDE but buslogic. Then detach and re-attache the VMDK:
http://kb.vmware.com/selfservice/microsites/search.do?language=en_US&cmd=displayKC&externalId=1016192

19. If the server is a Windows 2003 or newer server, or you P2V’d using the cold clone disk you will have to add a new adapter,
o For Windows 2003/2008/R2: remove all E1000 adapters on Windows 2000+ VM’s and use VMXNET3,
o For Windows 2000 use E1000.
Click Add, select Ethernet Adapter and change the type to VMXNET3. Finally select the desired network to connect to.



20. From the assign the correct VLAN to each virtual NIC, enable one at a time to know the correct one for each VLAN – they will become active in Control Panel once connected:

21. Power off and remove all COM Ports, Floppy Drives and USB Controllers, once complete power on the server:

22. From Add/Remove Programs remove all HP components except from Data Protector. Once completed reboot the server. You may have to kill a stuck service using task manager if the HP Insight Agents are in a Stopping State, look for cqmgserv.exe.

23. Manually remove the HP Network Team Adapter from Device Manager:

24. Take a snapshot of the Virtual Machine.
25. Download and run the ‘renewusb_2k.cmd’ (available here: http://cb-net.co.uk/downloads/devcon.zip) script to cleanup hidden/now invalid devices.
26. If server is a HP server download (available here: http://cb-net.co.uk/downloads/HPPSPCleaner.exe). Credits for this tool http://ctxadmtools.musumeci.com.ar/HPPSPCleaner/HPPSPCleanerDownload.html.

Check network connectivity, check network connectivity x-chassis’ and x-host
27. Delete static route from ESXi server (modify to suit the route you created earlier!):
esxcfg-route -d 172.20.20.141/32 10.144.120.100
28. Delete the route from the Windows Host
29. Delete the snapshot you created earlier.

30. If this is a Citirx server perform the following additional actions:
a. To ensure users cannot access VMware Tools from the system tray or control panel:
1. Go to C:\Program files\VMware\VMware Tools .
2. Right-click VMControlPanel.cpl properties and choose Security.
3. Click Advanced and deselect Allow inheritable permissions.
4. Click Deny for Read and Execute and Read for the users
5. Log in as an Administrator.
6. Right-click on the VMware Tools system tray icon.
7. Choose Disable.
8. In the registry editor, delete the VMware Tools key under
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run
b. Install WindowsServer2003-KB978243-x86-ENU.exe from P2V folder.
c. Set /NoExecute=OptIn in the boot.ini file if the Citrix server is x86.
d. Again, for Citrix Ensure that WindowsServer2003-KB2279561-x86-ENU.exe is installed (available in P2V folder) – this resolves stop 0x00000050 errors when using user mode printer drivers:

e. If server is a Citrix server adjust the page file to be RAM x 2 + 100MB (or if equal to/above 8GB RAM then RAM + 100MB)
f. If you have modified the PageFile and extended the System drive run PageDefrag to create a contagious page file.
g. If server is a Citrix server set services back to the correct start-up value:

h. Finally, in order to ensure user profiles are not corrupted:
1. Access the Windows Registry. Choose Start > Run, then type regedit. The Registry Editor window opens.
2. Navigate to HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\NetworkProvider\Order\.
3. Right-click ProviderOrder and choose Modify. In the Edit String Value dialog box, edit the value data string and remove the word hgfs, vmhgs, or vmhgfs).
o If the value data string contains LanmanWorkstation,hgfs, LanmanWorkstation,vmhgs, or LanmanWorkstation,vmhgfs, change it to LanmanWorkstation.
o If the value data string contains only hgfs or vmhgfs, erase it and leave the value data string empty.
4. Click OK.
5. Close the registry editor. Choose File > Exit.
Reboot the virtual machine.
31. If server is Windows 2003+ use Network Load Balancer MMC tool to re-add host, for Windows 2000 manually reconfigure the host. Including adding the secondary IP address to the host.
32. If server is a Windows 2003 server power off VM and configure Hardware Instruction Set and MMU virtualisation. Under the properties of the VM select the ‘options’ tab, then select CPU/MMU Virtualisation options. Select the value to suit your environment.

33. Again, if the server was a HP server, Delete the following registry keys:
Ø HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\CPQTeamMP
Ø HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\CPQTeam
Ø HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\cpqasm2
Ø HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\CpqCiDrv
Ø HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\CpqCiDrv\Security
34. Remove any HP Network Utility bindings from the VM NICs

35. Configure LAN interface power management options (disable power management!):

36. Move VM to the correct resource pool and adjust resource pool shares accordingly
37. Confirm that the following DWORD value is set to HEX 3C:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\services\Disk\TimeOutValue
38. Test server/application.




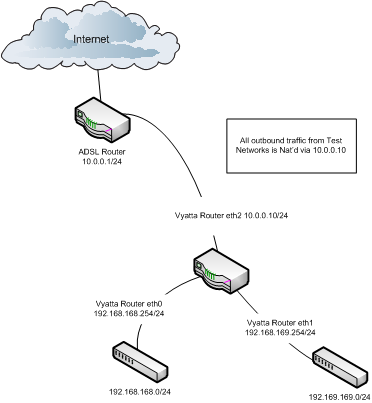
 In order to implement the above configuration on the Vyatta virtual router follow the configuarion steps outlined below. For reference the default username / password is vyatta / vyatta.
In order to implement the above configuration on the Vyatta virtual router follow the configuarion steps outlined below. For reference the default username / password is vyatta / vyatta.